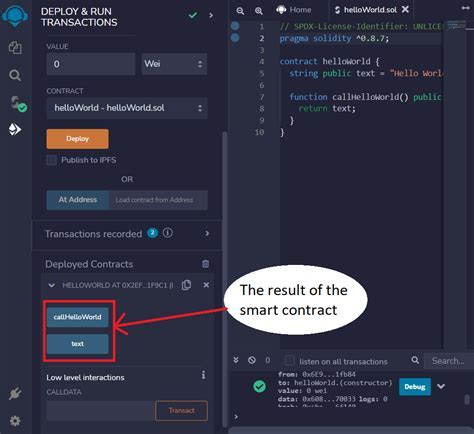
The World of Signatures: Understanding Adapter Signatures
In the realm of blockchain technology, signatures play a crucial role in verifying the authenticity and ownership of digital assets. Two types of signatures are often discussed: public-key signatures (also known as asymmetric signatures) and private-key signatures. Today, we’re going to explore an advanced type of signature that’s commonly used in cryptocurrency transactions: adapter signatures.
Public-Key Signatures
A public-key signature is a type of cryptographic signature that uses the recipient’s private key to sign a message. The process involves:
- The sender calculates a hash of the message and sends it along with their public key.
- The recipient receives the message and computes its hash using their private key.
- Using the recipient’s private key, they verify that the calculated hash matches the original message.
Example: Imagine you want to send $100 to your friend. You create a message saying “You sent $100” and sign it with your public key (a unique identifier). Your friend receives the message, uses their private key to verify the signature, and confirms that the message indeed says they received $100 from you.
Private-Key Signatures
A private-key signature is similar to a public-key signature, but instead of sending the entire message, the sender only signs a single element (such as the recipient’s name or some other identifying information). This approach has several advantages:
- Scalability: Private-key signatures can handle larger amounts of data without sacrificing security.
- Flexibility: You can create multiple private-key signatures with the same public key, making it easier to manage and track your digital assets.
Example: Let’s say you want to send a message that contains some identifying information (such as your name) along with $1 You would sign the entire message using your public key and then use a separate private key to attach an identifier (e.g., “John Doe”).
Adapter Signatures
Now, let’s dive into adapter signatures, which are used in cryptocurrency transactions.
What is a Signature Adapter?
An adapter signature is a type of digital signature that combines the security benefits of private-key signatures with the scalability advantages of public-key signatures. In other words, it allows you to send data without having to store your private key or sign the entire message.
How Does the Signature Adapter Work?
Here’s a simplified example:
- You want to send some data (e.g., $100) to someone using adapter signatures.
- You create two adapter signatures: one public and one private.
- When sending the data, you use your public signature to sign it.
- The recipient receives the signed message and uses their private key to verify the signature.
Example
Imagine you’re an exchange operator, and you want to send $100 to a user. You create two adapter signatures: Public Signature A (PSA) and Private Signature B (PSB). PSA is used for sending data, while PbSb is used for signing.
- You generate Public Signature A ($100 signatures).
- The recipient generates Private Signature B (signs the $100 amount).
- When they receive the message with PSA, they verify that the calculated hash matches the original $100.
- To send the data, you use PSA to sign it and include it in the transaction.
Security Benefits
Adapter signatures offer several security benefits over traditional private-key signatures:
- Decentralization

: Adapters enable decentralized transactions without requiring a central authority to manage private keys.
- Flexibility: You can create multiple adapter signatures with different public keys, making it easier to track and manage your digital assets.