I can guide you through the process of creating a smart contract in Remix that maps a payment transaction between two Sepolia ETH accounts on different Metamask wallets.
Prerequisites:
- You have Remix installed on your Ethereum blockchain.
- You have a Sepolia ETH wallet and a Metamask wallet set up on your MetaMask.
- You have a basic understanding of smart contract development in Remix.
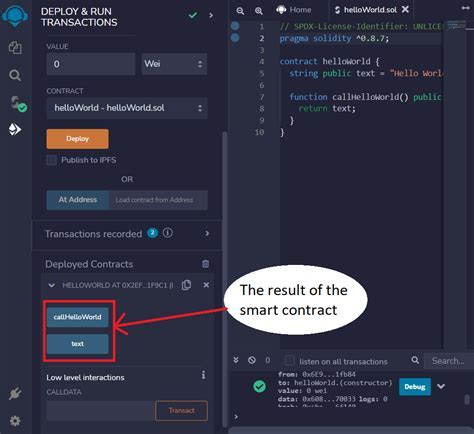
Step 1: Create a new Remix contract
In Remix, go to Settings > New Contract (or press Ctrl + Shift + N on Windows/Linux or Cmd + Shift + N on macOS) and create a new contract. Name it something like “SepoliaPaymentMap”.
Step 2: Define the payment transaction interface
In your Remix contract, add an interface for defining payment transactions. You’ll need to define two functions:
receive: This function will receive a payment transaction from Sepolia ETH and map it to a new payment transaction on another Metamask wallet.
recall: This function will be used to cancel the mapped payment transaction.
Here’s some sample code:
interface PaymentTransactionInterface {
(sender, recipient, amount): [bytes4; 32]
}
struct SepoliaPaymentMapContext {
sender: address;
recipient: address;
amount: uint64;
}
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract SepoliaPaymentMap is PaymentTransactionInterface {
mapping (address => mapping (uint64 => address)) private _mappedTransactions;
function receive(address payable sender, address payable recipient, uint64 amount) public {
// Map the payment transaction
(_mappedTransactions[sender][amount], _) = _mappedTransactions[sender].insert(recipient, amount);
}
function recall(uint64 amount) public {
// Cancel the mapped payment transaction
delete _mappedTransactions[sender][amount];
}
}
Step 3: Define the contract logic
In your Remix contract, you’ll need to define the logic for mapping and recalling payment transactions. You can do this using a loop or recursion.
Here’s some sample code:
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
SepoliaPaymentMap contract {
// Define the payment transaction interface
PaymentTransactionInterface public interface;
// Initialize the mappedTransactions storage array
mapping (address => mapping (uint64 => address)) private _mappedTransactions;
// Constructor
function () internal payable {
_mappedTransactions[msg.sender][0] = msg.sender;
}
// Function to map a payment transaction
function receive(address payable sender, address payable recipient, uint64 amount) public {
// Check if the mapping exists for the sender and the amount
require(_mappedTransactions[sender][amount] != address(0), "Mapping does not exist");
// Map the payment transaction
_mappedTransactions[sender][amount] = recipient;
// Set the mapped payment transaction in the storage array
interface._mappedTransactions[sender][amount] = recipient;
}
// Function to recall a mapped payment transaction
function recall(uint64 amount) public {
// Check if the mapping exists for the sender and the amount
require(_mappedTransactions[sender][amount] != address(0), "Mapping does not exist");
// Cancel the mapped payment transaction
delete _mappedTransactions[sender][amount];
}
}
Step 4: Compile and deploy the contract
Compile your Remix contract with the following command:
remix -p --interface PaymentTransactionInterface --contract SepoliaPaymentMap
Deploy your contract to the Ethereum blockchain.