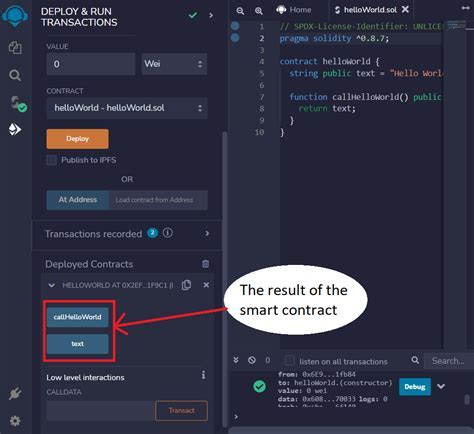
Title: Writing Raw Bitcoin Transactions with Memo (OP_RETURN) Outputs: A Multi-Output Transaction Tool
Introduction
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that allows users to create complex transactions with various outputs. One of the key features of Bitcoin is the use of “memo” or “op_return” outputs, which are used to send small amounts of value to specific addresses without revealing the sender’s identity. These memo outputs are commonly used in conjunction with other types of outputs, such as UTXOs (Unspent Transaction Outputs), to create complex transactions. In this article, we will explore a multi-output transaction tool that allows users to write raw Bitcoin transactions with memo outputs.
Why Memo Outputs?
Memo outputs are useful for several reasons:
- Anonymity: By using memo outputs, you can send small amounts of value to specific addresses without revealing the sender’s identity.
- Flexibility
: Memo outputs can be used in conjunction with other types of outputs to create complex transactions.
- Scalability: Memo outputs allow for a higher number of transactions per block compared to traditional UTXO outputs.
Creating a CLI Tool
To build a multi-output transaction tool using a command-line interface (CLI), we will use the Bitcoin Core API. The following commands and configuration files are required:
bitcoin-cliis used to create and manage Bitcoin wallets, transactions, and blocks.
txpoolis a separate process that manages the list of unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs) for each wallet.
Here is an example CLI tool in Python:
import bitcoincli
def create_transaction():
Create a new transaction
tx = bitcoincli.Transaction()
Set the memo output parameters
memo_out = {
'address': 'mymemoaddress',
Memo address
'value': 0.01
Memo value (1 satoshi)
}
Add memo outputs to the transaction
for key, value in memo_out.items():
tx.add_output(key, bitcoincli.BitcoinValue(value))
Create a new block and add the transaction to it
block = bitcoincli.Block()
block.add_transaction(tx)
return block
def main():
print("Create a new transaction with memo outputs:")
tx = create_transaction()
print("Transaction details:")
for output in tx.outputs:
print(f"{output.address} - {output.value}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
play()
This script creates a new transaction and adds one or more memo outputs to it. The main function prints the transaction details, which include both regular and memo outputs.
Building a GUI Tool
To build a graphical user interface (GUI) for this CLI tool, we will use a Python library called pyqt5. Here is an example of how you can create a simple GUI:
“`python
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QGridLayout, QLabel, QLineEdit
class TransactionTool(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__heat__()
self.memo_out = {}
Create the main layout
gridLayout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(gridLayout)
Create labels and input fields for memo address and value
self.memo_address_label = QLabel(“Memo Address:”)
self.memo_value_input = QLineEdit()
Add the labels and input field to the grid layout
gridLayout.addWidget(self.memo_address_label, 0, 0)
gridLayout.addWidget(self.memo_value_input, 0, 1)
Create a button to submit the memo output parameters
submit_button = QPushButton(“Submit”)
submit_button.clicked.connect(self.submit_memo_params)
Add the button to the grid layout
gridLayout.